|
Here we have a set of cumulative probability calculators aiming to compute a probability for the following distribution functions: Normal, Lognormal, Gamma, Exponential, Student’s, Binomial, Geometric, Negative Binomial and Poisson. Information about these distributions are provided in the section "Summary of Distribution Functions" below in this page.
To calculate a probability, just follow the 3 steps below:
Step 1) Select a probability distribution function:
Step 2) Enter the parameter(s) for the selected distribution.
Step 3) Specify what you want to calculate:
I wish to know the odds of getting a number
than the value
Help us to develop the tool. Make a donation.
Summary of Distribution Functions
The Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) is the probability that the random variable X will take a value less than or equal to x. The following table summarizes common continuous and discrete distributions, showing the cumulative function and its parameters. In this table, the continuous distributions are: Normal, Lognormal, Gamma, Exponential, and Student’s. The discrete distributions are: Binomial, Geometric, Negative Binomial and Poisson.
Normal
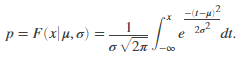
Returns the probability 'p' that a single observation from a Normal distribution with parameters µ and σ falls in the interval (-∞,x]. The normal distribution is a two-parameter family of curves. The first parameter, µ, is the mean. The second parameter, σ, is the standard deviation.
|
Lognormal
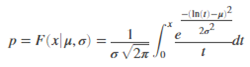
Returns values at x of the Lognormal cumulative distribution function with distribution parameters µ and σ, where µ and σ are the mean and standard deviation, respectively, of the associated normal distribution. |
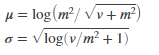
A lognormal distribution with mean m and variance v has parameters µ and σ.
|
Gamma
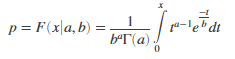
Returns the Gamma cumulative distribution function at value x using the corresponding shape parameters in a and scale parameters in b.
|
Exponential
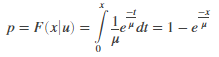
Computes the Exponential cumulative distribution function at value x using the corresponding mean parameter µ.
|
Student's
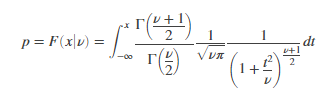
Computes a Student’s cumulative distribution function at value x where ν is the degrees of freedom and Γ( · ) is the Gamma function. The result p is the probability that a single observation from the t distribution with ν degrees of freedom will fall in the interval [–∞, x].
|
Binomial
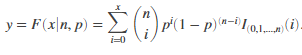
Computes a binomial cumulative distribution function at value x using the corresponding number of trials in N and probability of success for each trial in p.
|
Geometric
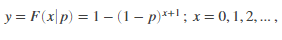
Computes a Geometric cumulative distribution where p is the probability of success, and x is the number of failures before the first success. The result y is the probability of observing up to x trials before a success, when the probability of success in any given trial is p.
|
Negative Binomial
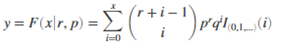
Computes the Negative binomial cumulative distribution at value x using the corresponding number of successes (R) and probability of success in a single trial (p).
|
Poisson
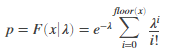
Returns the Poisson cumulative distribution function at value x using the corresponding mean parameter in lambda. |
Find us on 
Remember you can access this website in your mobile phone and add it to your favorites.
|